Getting Started with Kubernetes: A Beginner's Guide
- Daniel Cardozo
- Devops , Kubernetes
- 28 de septiembre de 2024
Tabla de Contenidos
Kubernetes, often abbreviated as K8s, is an open-source platform designed to automate deploying, scaling, and managing containerized applications. As more applications adopt microservices architectures, Kubernetes provides a highly scalable solution to manage and orchestrate containers in production.
What is Kubernetes?
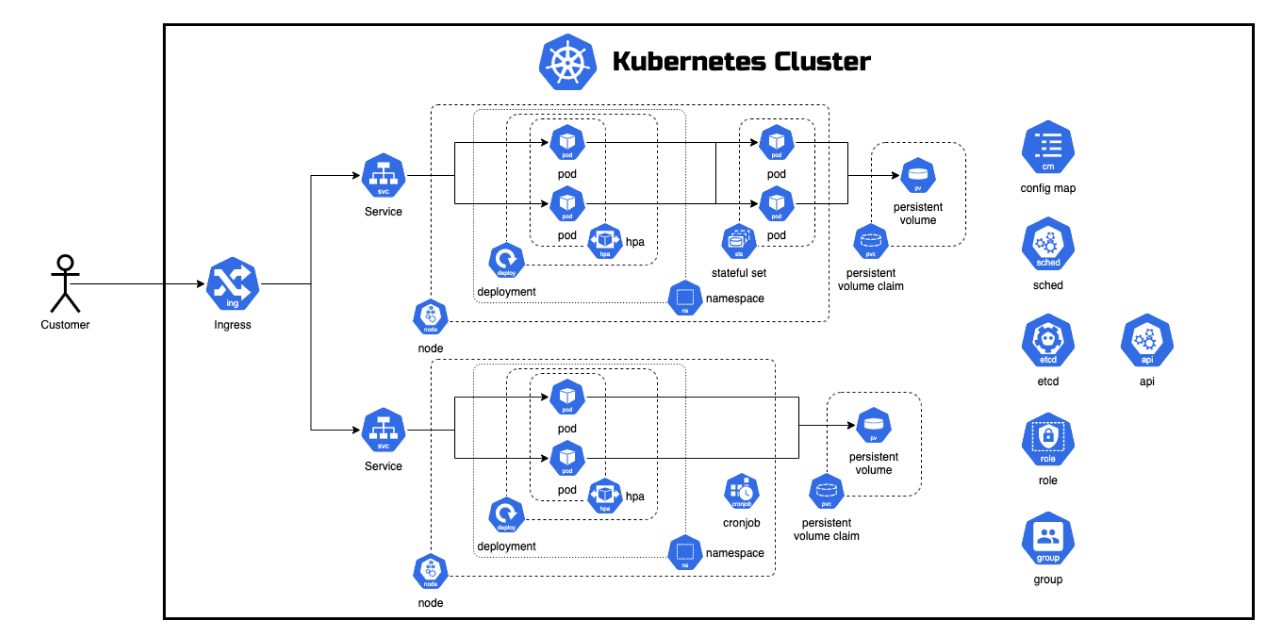
Kubernetes helps in managing a large number of containers in various environments. It automates container deployment, scaling, and operations by grouping containers into logical units, ensuring they are efficiently and reliably managed.
Key Components of Kubernetes
- Pods: The smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes, a Pod can contain one or more containers.
- Nodes: Physical or virtual machines running Kubernetes, responsible for hosting and managing Pods.
- Clusters: A set of nodes that run containerized applications.
Why Use Kubernetes?
Kubernetes helps businesses achieve:
- Scalability: Automatically scale your application based on traffic.
- High Availability: Ensures that your services remain available even during node failures.
- Flexibility: Works with various cloud providers, enabling hybrid and multi-cloud deployments.
Tip: Kubernetes can be integrated with monitoring tools like Prometheus and Grafana for tracking the performance and health of your clusters.
How to Deploy an Application in Kubernetes
- Create a Docker Image: First, containerize your application using Docker.
- Write Kubernetes YAML Files: Define the deployment and service configurations in
.yamlfiles. - Deploy to a Cluster: Use
kubectlto deploy your application.kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml kubectl apply -f service.yaml
